 PCR is fundamental to many of the procedures used in genetic testing, research, including analysis of ancient samples of DNA and identification of infectious agents. Using PCR, copies of very small amounts of DNA sequences are exponentially amplified in a series of cycles of temperature changes.
PCR is fundamental to many of the procedures used in genetic testing, research, including analysis of ancient samples of DNA and identification of infectious agents. Using PCR, copies of very small amounts of DNA sequences are exponentially amplified in a series of cycles of temperature changes. A PCR (polymerase chain reaction) test is a lab technique that amplifies (creates more copies) of genetic material (DNA). Healthcare providers can use PCR to test for infectious diseases, to look for genetic changes in tumors or to diagnose genetic diseases.
A PCR (polymerase chain reaction) test is a lab technique that amplifies (creates more copies) of genetic material (DNA). Healthcare providers can use PCR to test for infectious diseases, to look for genetic changes in tumors or to diagnose genetic diseases.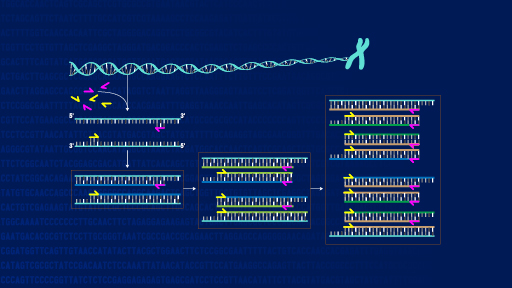 Sometimes called "molecular photocopying," the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a fast and inexpensive technique used to "amplify" - copy - small segments of DNA.
Sometimes called "molecular photocopying," the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a fast and inexpensive technique used to "amplify" - copy - small segments of DNA. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is used to make numerous copies of a specific segment of DNA quickly and accurately, enabling experiments in molecular biology, forensic analysis, evolutionary biology, and medical diagnostics.
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is used to make numerous copies of a specific segment of DNA quickly and accurately, enabling experiments in molecular biology, forensic analysis, evolutionary biology, and medical diagnostics.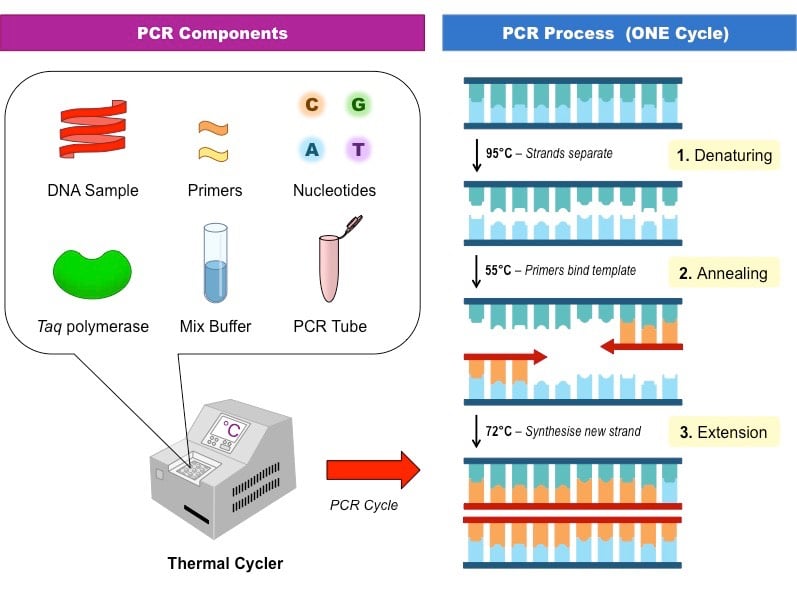 Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a nucleic acid amplification technique used to amplify the DNA or RNA in vitro enzymatically.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a nucleic acid amplification technique used to amplify the DNA or RNA in vitro enzymatically.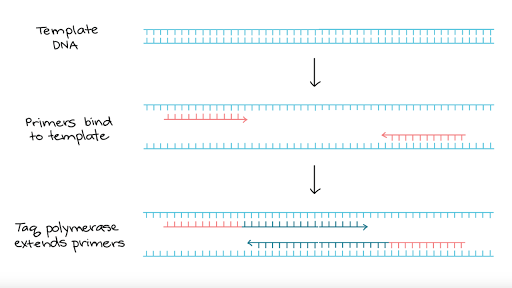 Polymerase chain reaction, or PCR, is a technique to make many copies of a specific DNA region in vitro (in a test tube rather than an organism). PCR relies on a thermostable DNA polymerase, Taq polymerase, and requires DNA primers designed specifically for the DNA region of interest.
Polymerase chain reaction, or PCR, is a technique to make many copies of a specific DNA region in vitro (in a test tube rather than an organism). PCR relies on a thermostable DNA polymerase, Taq polymerase, and requires DNA primers designed specifically for the DNA region of interest.